Constant Marginal Costs Occur When Each Individual Unit Costs
Setting MR equal to MC to determine the profit-maximizing quantity. The same to produce as the previous one.
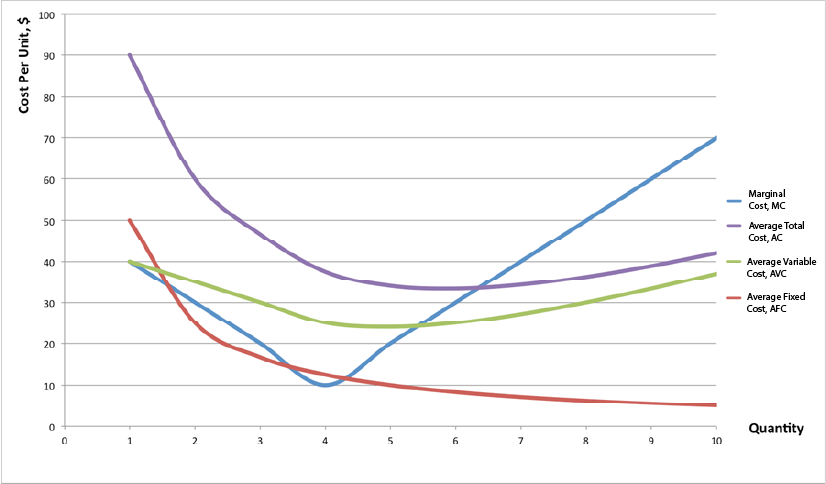
Module 8 Cost Curves Intermediate Microeconomics
In the previous lesson when we used a constant heat rate to derive a marginal cost we had assumed this type of cost.
. 27 - 3Q 10 or Q 567. When will a firm find the optimal level of. The marginal cost for one additional unit produced is either 5 for any unit except the 101 st 201 st etc.
Efficient collective decision-making marginal cost pricing and quadratic voting. DTC Q dQ b. Fixed costs of production are constant occur regularly and do not change in the short-term.
Where the marginal costs would be 1005. Less than the previous one to produce. B more than the previous one.
A firm has a fixed production cost of 5000 and a constant marginal cost of production of 500 per unit produced. Marginal cost is a constant 10. The marginal cost of introducing a new product line would be 10000.
A Assume that the monopolist can engage in first-degree price discrimination using a two-part tariff. Marginal Cost Change in Costs Change in Quantity Marginal cost represents the incremental costs incurred when producing additional units of a good or service. 42 which is just a constant.
To find the profit-maximizing price substitute this quantity into the demand equation. What is the firms total cost function. Marginal Cost Calculator This marginal cost calculator allows you to calculate the additional cost of producing more units using the formula.
Constant marginal costs occur when each individual unit costs A. Since the cost is the same for every single unit produced it is considered a constant. Constant marginal cost is the total amount of cost it takes a business to produce a single unit of production if that cost never changes.
TC Q a b Q. Servicing one additional customer would cost 2000. Consider a monopolist facing a demand curve from an individual consumer of P 120 - q where P is per-unit price and q is the quantity demanded.
The monopolists maximizing output occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The monopolist has a fixed cost of 100 and a constant marginal cost of 30 per unit. 61Constant marginal costs occur when production of each individual unit costs.
41 where TC is total cost Q is total output MWh and a and b are constants then the marginal cost of electricity production is found by taking the derivative of the total cost function. A less than the previous one. In this example marginal costs for various activities exist.
The variable part of the equation to estimate costs is the total volume of items that the company produces. A firm has a fixed production cost of 5000 and a constant marginal cost of production of 500 per unit produced. C the same as the previous oneD more than the next one.
Marginal costs are a function of the total cost of production which includes fixed and variable costs. More than the previous one to produce. It is calculated by taking the total cha.
What is the firms total cost function. Public Choice 172 1 45-73. P 27 15567 185.
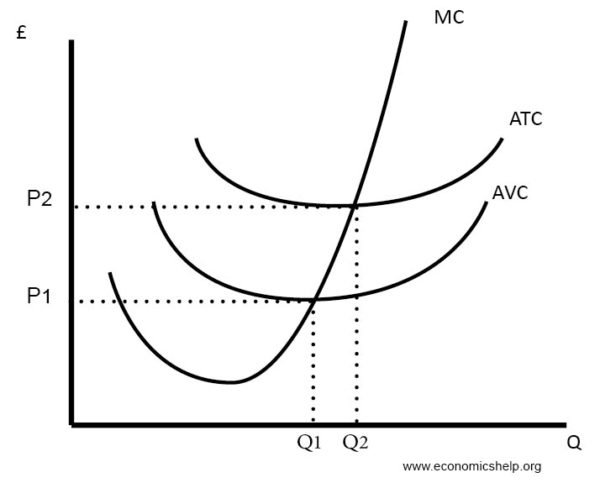
Diagrams Of Cost Curves Economics Help
/MarginalRateofSubstitution3-a96cfa584e1440f08949ad8ef50af09a.png)
Marginal Rate Of Substitution Mrs Definition
The Firm Under Competition And Monopoly

Long Run Supply When Industry Costs Aren T Constant Video Khan Academy
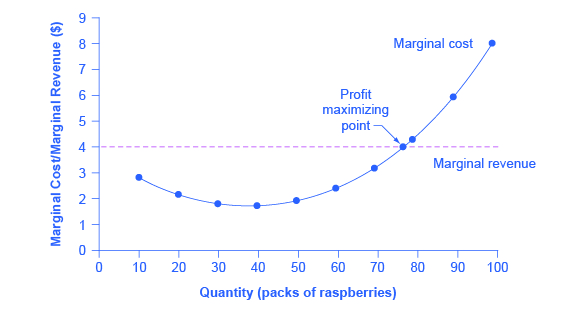
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions Principles Of Economics
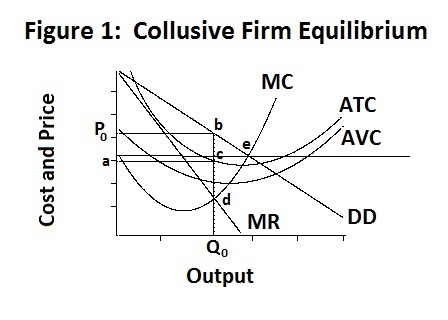
Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium

Increasing Marginal Costs And The Efficiency Of Differentiated Feed In Tariffs Sciencedirect
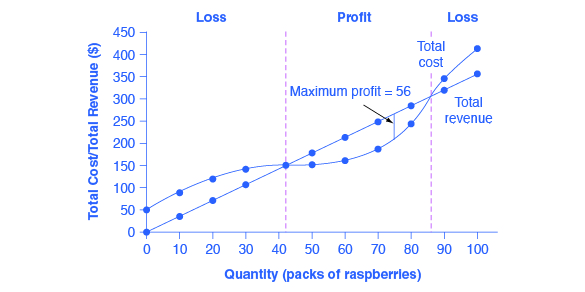
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions Principles Of Economics
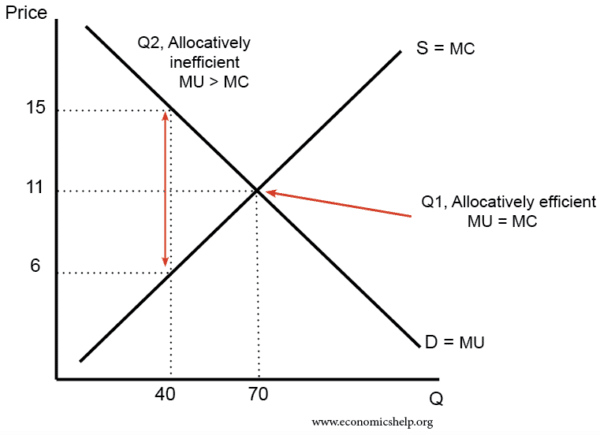
Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help
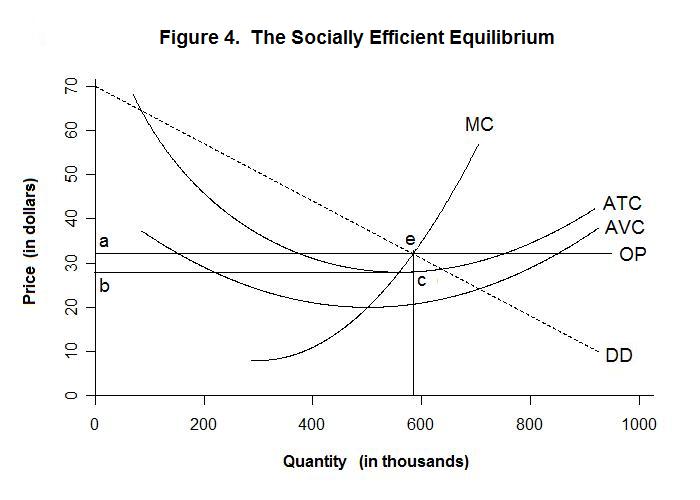
Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium

Marginal Costs An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
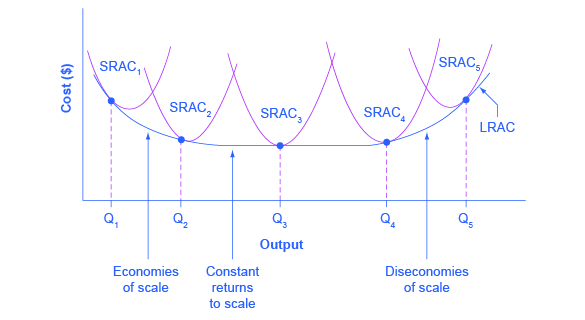
Economies Of Scale Microeconomics
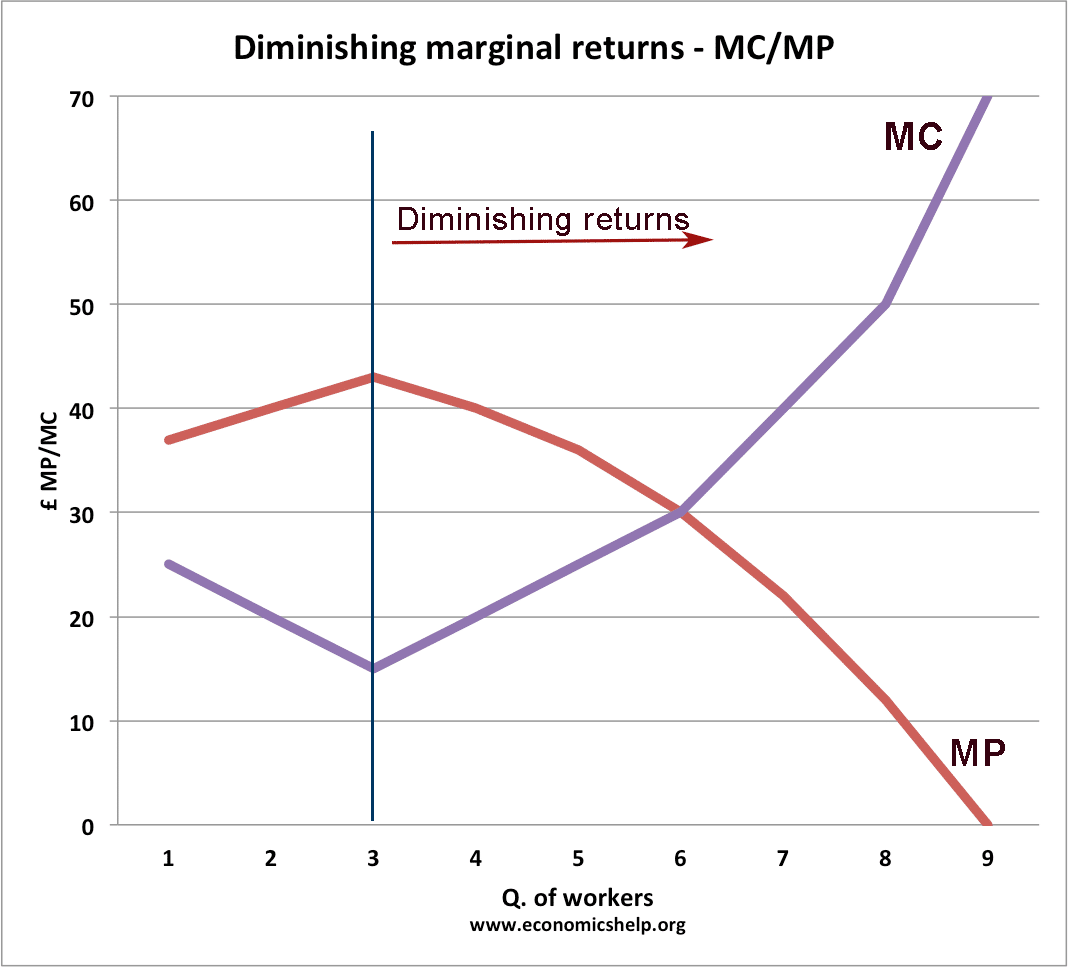
The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Returns Economics Help
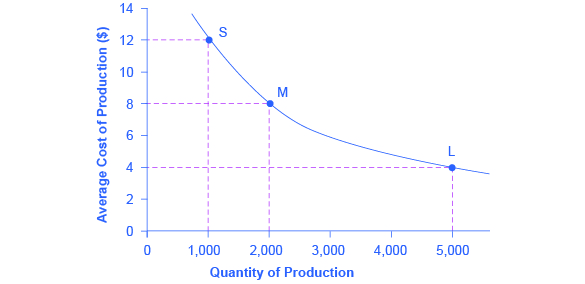
Economies Of Scale Microeconomics
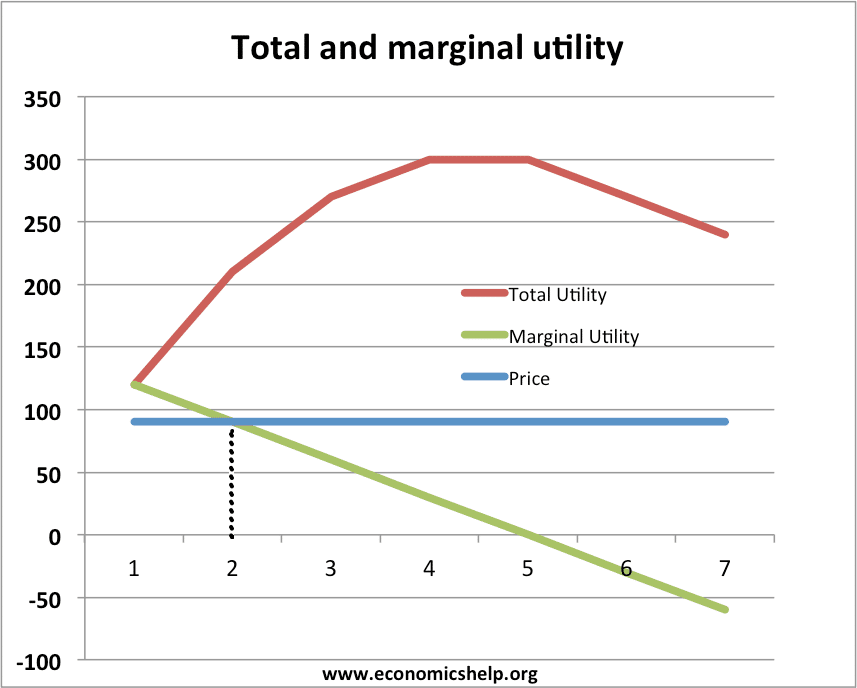
Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help

Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium
/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)
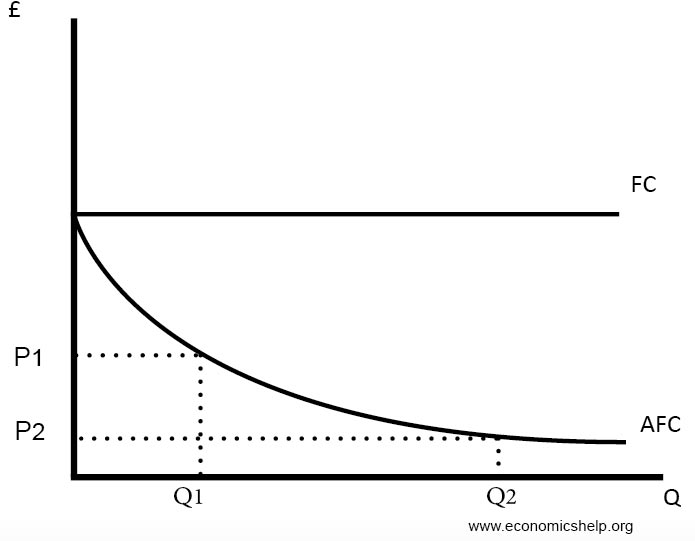
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)